The Configuration page is used to display and manage the basic configuration of the receiver. It is divided into three boxes: Common configuration, Status and Endpoint type.
Configuration
The first box contains information about the sender, its database, and security.
Basic
Basic configuration is used to display and change the metadata of the module - the name and the description.
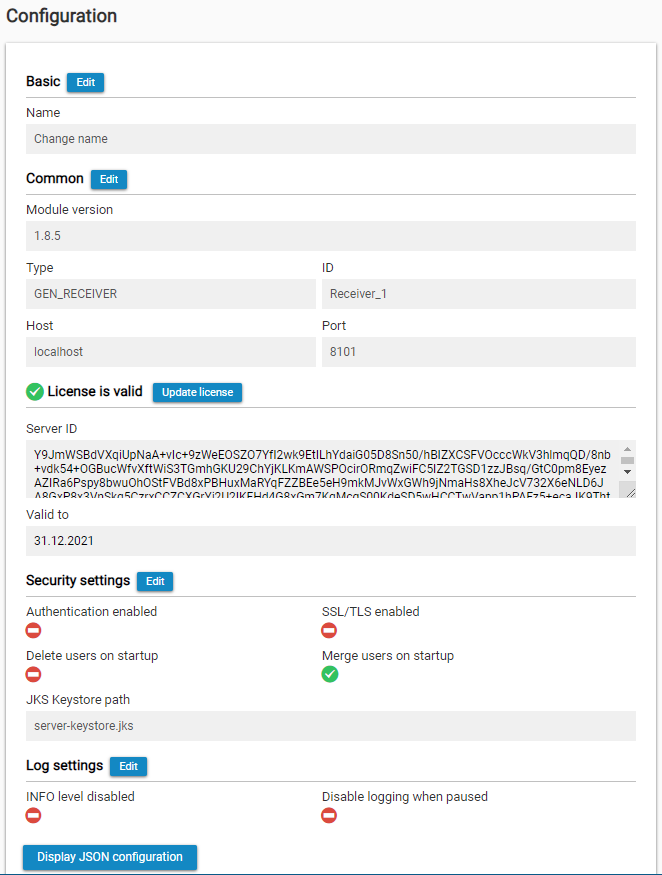
Common
In the common configuration, users can see the type of the module, its ID, host and port where the module is running. They can change the port by clicking on Edit. After applying the changes, the module will be started on the selected port. Please note that this port has to be available - not occupied by other module or another service, and opened in the firewall.
The port can be changed by domain administrator and IoT administrator in single-domain environment, and by domain administrator who is also global administrator in multi-domain environment.
For more information about each option, please see this page.
License
Administrators can edit the license key directly from the IoT Console.
Valid to: date untill license for module is valid
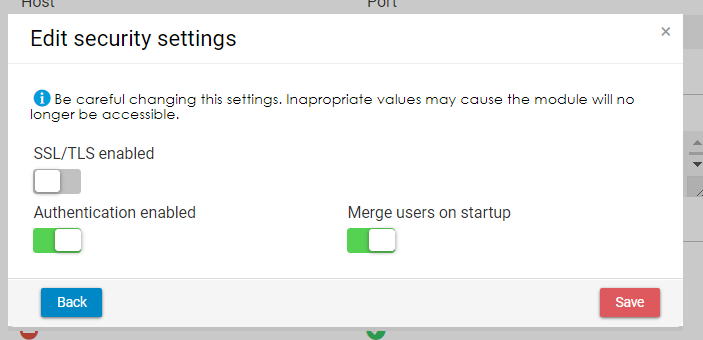
Security settings
Additionally, administrators can change the security settings:
- Enable or disable authentication
- Enable or disable SSL/TLS
- Enable or disable merging of users on startup
This functionality is available to domain administrator and IoT administrator in single-domain environment, and to domain administrator who is also global administrator in multi-domain environment.
After enabling SSL/TLS via the IoT Console, it is necessary to create a new keystore, or modify the default keystore.js, and add the certificate. This has to be done to all modules where the SSL/TLS is enabled. You can learn more about adding SSL/TLS here.
Status
The Status box displays the status of the receiver.
The button Reload is used to reload the receiver after changes. The button Pause is used to temporarily suspend the receiver. When paused, the receiver won't process any new data. After clicking on Resume, the receiver will start working again.
The date and time of the last update can be found at the bottom of this box.
Endpoint Type
The most important box allows the user to change the endpoint settings of the receiver. There are five different endpoint types:
- HTTP POST Consume
- MQTT Subscribe
- MQTT Broker
- UDP Server
- WebSocket Client
- MC TCP Client
- MC serial Client
- JMS Subscribe
- RTSP Client
- Kafka Consumer
- Custom
Each endpoint type is defined by a set of parameters.
Additionally, the user can also see the actual status of the endpoint - whether it was correctly started, connected to the supporting service (e.g. MQTT broker) etc.
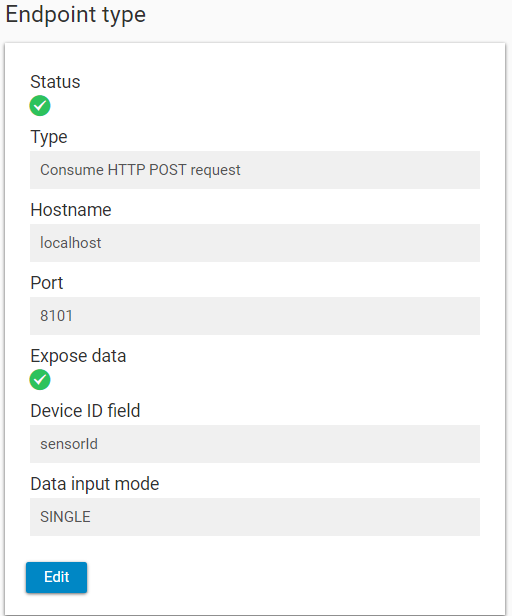
HTTP POST Consume
This endpoint type is used when the devices (sensors) are sending the data via standard HTTP method POST by using TCP/IP connection. Both HTTP an HTTPS are supported.
Following parameters are used by this endpoint type:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Device ID field | The name of the element which contains the unique identification of the device (sensor). In case the field is not located on the first level, it is possible to specify the path (e.g. device.sensorId ). |
| Receiver Input Mode | Single or Bulk. For Single, each message contains exactly one set (row) of data. For Bulk, the message can contain more sets (rows). |
When enabled, a device ID specified in field will be assigned to all data sent to this receiver. This allows processing data from devices that are unable to specify the device ID by themselves. If the received data contains the device ID, it will be overridden. | |
| Path to data element | Specifies "data" element path in BULK mode. Example: root.data (for XML) |
| Message Content Type | Defines in which format will be the data sent to the receiver. For more information, see the chapter below. |
| Body limit | The maximum size of the body of the message (in bytes) |
| Expose Data | Flag indicating if endpoints GET /data and DELETE /data should be exposed |
When sending the data to the receiver, make sure that you include the endpoint /data in the target URL (http://URLofReceiver/data).
MQTT Subscribe
MQTT Subscribe can be used to subscribe to an MQTT broker. This type of receiver automatically collects all data, which are published with the selected topic.
Following parameters are used by this endpoint type:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Host | URL or IP address of the MQTT Broker |
| Port | Port of the MQTT Broker |
| Message Content Type | Defines in which format will be the data sent to the receiver. For more information, see the chapter below. |
| Topic | Topic to which should the receiver subscribe |
| QOS | Quality of Service
|
| Device ID field | The name of the element which contains the unique identification of the device (sensor). In case the field is not located on the first level, it is possible to specify the path (e.g. device.sensorId). |
| Force Device ID | When enabled, a device ID specified in field will be assigned to all data sent to this receiver. This allows processing data from devices that are unable to specify the device ID by themselves. If the received data contains the device ID, it will be overridden. |
| Receiver Input Mode | Single or Bulk. For Single, each message contains exactly one set (row) of data. For Bulk, the message can contain more sets (rows). |
| Body limit | The maximum size of the body of the message (in bytes) |
| Expose data | Flag indicating if endpoints GET /data and DELETE /data should be exposed |
MQTT Broker
By using this setting, an MQTT Broker will be launched on a specified port. Devices (sensors) can then subscribe to this Broker, which receive the data and process them.
Following parameters are used by this endpoint type:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Host | URL or IP address of this MQTT Broker In cases, when the external IP does not match the actual IP (such as AWS instances), it might be necessary to use IP 0.0.0.0 |
| Port | The port on which the MQTT Broker will be launched. It has to be different than the port of the receiver. The port of the receiver will be used for the management and the port of the MQTT Broker will be used for the data connection. |
| Message Content Type | Defines in which format will be the data sent to the receiver. For more information, see the chapter below. |
| Device ID field | The name of the element which contains the unique identification of the device (sensor). In case the field is not located on the first level, it is possible to specify the path (e.g. device.sensorId ). |
| Force Device ID | When enabled, a device ID specified in field will be assigned to all data sent to this receiver. This allows processing data from devices that are unable to specify the device ID by themselves. If the received data contains the device ID, it will be overridden. |
| Receiver Input Mode | Single or Bulk. For Single, each message contains exactly one set (row) of data. For Bulk, the message can contain more sets (rows). |
| Body limit | The maximum size of the body of the message (in bytes) |
| Expose data | Flag indicating if endpoints GET /data and DELETE /data should be exposed |
UDP Server
This type of endpoint allows the user to set up a UDP Server on a specified port. Devices can connect to this server and send messages.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Host | URL or IP address of this UDP Server |
| Port | The port on which the UDP Server will be launched. It is recommended to use a different port than the port of the receiver. In that case, the port of the receiver will be used for the management and the port of the UDP Server will be used for the data connection. |
| Message Content Type | Defines in which format will be the data sent to the receiver. For more information, see the chapter below. |
| Device ID field | The name of the element which contains the unique identification of the device (sensor). In case the field is not located on the first level, it is possible to specify the path (e.g. device.sensorId). |
| Force Device ID | When enabled, a device ID specified in field will be assigned to all data sent to this receiver. This allows processing data from devices that are unable to specify the device ID by themselves. If the received data contains the device ID, it will be overridden. |
| Receiver Input Mode | Single or Bulk. For Single, each message contains exactly one set (row) of data. For Bulk, the message can contain more sets (rows). |
| Body limit | The maximum size of the body of the message (in bytes) |
| Expose data | Flag indicating if endpoints GET /data and DELETE /data should be exposed |
WebSocket Client
By using the endpoint type, users can connect to a WebSocket server, which is publishing the messages.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Host | URL or IP address of the WebSocket Server |
| Port | Port of the WebSocket Server |
| Relative path to the endpoint published by the WebSocket Server | |
| When enabled, the client will try to connect via wss:// instead of ws:// | |
| Defines in which format will be the data sent to the receiver. For more information, see the chapter below. | |
The name of the element which contains the unique identification of the device (sensor). In case the field is not located on the first level, it is possible to specify the path (e.g. device.sensorId). | |
| Force Device ID | When enabled, a device ID specified in field will be assigned to all data sent to this receiver. This allows processing data from devices that are unable to specify the device ID by themselves. If the received data contains the device ID, it will be overridden. |
| Single or Bulk. For Single, each message contains exactly one set (row) of data. For Bulk, the message can contain more sets (rows). | |
| The maximum size of the body of the message (in bytes) | |
| Flag indicating if endpoints GET /data and DELETE /data should be exposed |
MC TCP Client
By using the endpoint type, users can connect to a PLC device as MC TCP Client.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Host | URL or IP address of the PLC device |
| Port | Port of the PLC device |
| Request interval (ms) | Interval of the request (in milliseconds) |
| Device name | Name of the device |
| Minimum device number | |
| Maximum device number | |
| Hexadecimal Input | Enables or disables the hexadecimal input |
| Switches between ASCII and BINARY mode | |
Sets the address type. ASCII mode:
Binary mode:
| |
| Data size | Switches between Bit and Word |
| Force Device ID | When enabled, a device ID specified in field will be assigned to all data sent to this receiver. This allows processing data from devices that are unable to specify the device ID by themselves. If the received data contains the device ID, it will be overridden. |
| Flag indicating if endpoints GET /data and DELETE /data should be exposed |
MC serial Client
By using the endpoint type, users can connect to a PLC device as MC serial Client.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| COM Port | COM Port of the PLC device |
| Baud rate | |
| Parity | Sets the parity type (none, even, odd) |
| Stop bits | |
| Data length | |
| Sets the flow control (none, RTS/CTS, Xon/Xoff) | |
| Request interval (ms) | Interval of the request (in milliseconds) |
| Device name | Name of the device |
| Minimum device number | |
| Maximum device number | |
| Hexadecimal Input | Enables or disables the hexadecimal input |
| Switches between ASCII and BINARY mode | |
Sets the address type. ASCII mode:
Binary mode:
| |
| Data size | Switches between Bit and Word |
| Force Device ID | When enabled, a device ID specified in field will be assigned to all data sent to this receiver. This allows processing data from devices that are unable to specify the device ID by themselves. If the received data contains the device ID, it will be overridden. |
| Flag indicating if endpoints GET /data and DELETE /data should be exposed |
JMS Subscribe
This type of receiver automatically collects all data, which are published with the selected topic.
Following parameters are used by this endpoint type:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Host | URL or IP address of the MQTT Broker |
| Port | Port of the MQTT Broker |
| Message Content Type | Defines in which format will be the data sent to the receiver. For more information, see the chapter below. |
| Topic | Topic to which should the receiver subscribe |
| Username | Username used for authentication |
| Password | Password used for authentication |
| Device ID field | The name of the element which contains the unique identification of the device (sensor). In case the field is not located on the first level, it is possible to specify the path (e.g. device.sensorId). |
| Force Device ID | When enabled, a device ID specified in field will be assigned to all data sent to this receiver. This allows processing data from devices that are unable to specify the device ID by themselves. If the received data contains the device ID, it will be overridden. |
| Receiver Input Mode | Single or Bulk. For Single, each message contains exactly one set (row) of data. For Bulk, the message can contain more sets (rows). |
| Body limit | The maximum size of the body of the message (in bytes) |
| Expose data | Flag indicating if endpoints GET /data and DELETE /data should be exposed |
RTSP Client
By using the endpoint type, users can connect to rtsp streams and can output images in defined interval.
For this endpoint to work, user need to download ffmpeg application. It can be downloaded here
Following parameters are used by this endpoint type:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path to FFMpeg binary | You need to provide address for external ffmpeg application. e.g. "c:\temp\ffmpeg\bin\ffmpeg.exe" or linux "/home/belladati/ffmpeg-n5.0-latest-linux64-gpl-5.0/bin/ffmpeg" |
| Capture frequency [seconds] | You will define time period in which will images be captured. |
| Image height (optional) | Set output image height. If not set, same diameter as stream has will be used. |
| Create folder for each stream (optional) | If multiple streams are defined, user can store each stream in its folder. Folder name will be taken from stream name |
| Store to filesystem (optional) | This will set, that output pictures will be stored on filesystem |
| Filesystem path | If Store to filesystem is set path to output file needs to set |
| Store to FTP (optional) | This will define, that output pictures will be stored on FTP |
| Hostname | If Store to FTP is set, hostname of FTP server needs to be set |
| Port | If Store to FTP is set, port of FTP server needs to be set |
| Username (optional) | If Store to FTP is set, username for FTP server can to be set |
| Password (optional) | If Store to FTP is set, password for FTP server can to be set |
| FTP directory | If Store to FTP is set, directory of FTP server needs to be set |
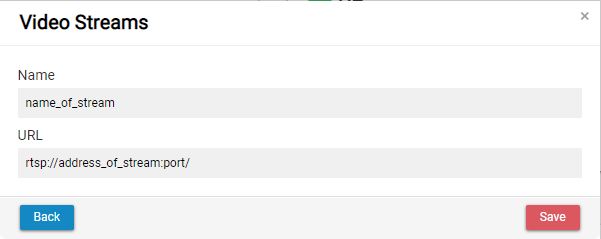
To add new Video Stream RTSP Client endpoint must be defined. New option will appear. Click Add to add one new stream.
You need to set name of your stream and its address and Save settings. You can add multiple streams for one receiver
AudioML
By using the endpoint type, users can connect to audio stream or audio file and analyze it using Fast Fourier Transformation. You can determine audio vibrations. You do not need to run another FFT transformation on Sender. Data are already transformated on receiver.
For this endpoint to work, user need to download ffmpeg application. It can be downloaded here
Following parameters are used by this endpoint type:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path to FFMpeg binary | You need to provide address for external ffmpeg application. e.g. "c:\temp\ffmpeg\bin\ffmpeg.exe" or linux "/home/belladati/ffmpeg-n5.0-latest-linux64-gpl-5.0/bin/ffmpeg" |
| Device ID Field | The name of the element which contains the unique identification of the device (sensor). In case the field is not located on the first level, it is possible to specify the path (e.g. device.sensorId ). |
| Force Device ID | When enabled, a device ID specified in field will be assigned to all data sent to this receiver. This allows processing data from devices that are unable to specify the device ID by themselves. If the received data contains the device ID, it will be overridden. |
| Path to data element | Specifies "data" element path in BULK mode. Example: root.data (for XML) |
| Audio Stream URL | Define address of stream or audio file |
| FFT Points | The amout of points used in Fast Fourier Transformations |
| Filesystem path | If Store to filesystem is set path to output file needs to set |
Kafka Consumer
By using this setting, an Kafka Consumer will be launched on a specified port. Devices (sensors) can then subscribe to this consumer, which receive the data and process them.
Following parameters are used by this endpoint type:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
URL or IP address and port of this Kafka Broker In cases, when the external IP does not match the actual IP (such as AWS instances), it might be necessary to use IP 0.0.0.0 | |
| Topic | What topic is listening on |
| Message Content Type | Defines in which format will be the data sent to the receiver. For more information, see the chapter below. |
| Device ID field | The name of the element which contains the unique identification of the device (sensor). In case the field is not located on the first level, it is possible to specify the path (e.g. device.sensorId ). |
| Force Device ID | When enabled, a device ID specified in field will be assigned to all data sent to this receiver. This allows processing data from devices that are unable to specify the device ID by themselves. If the received data contains the device ID, it will be overridden. |
| Receiver Input Mode | Single or Bulk. For Single, each message contains exactly one set (row) of data. For Bulk, the message can contain more sets (rows). |
| Body limit | The maximum size of the body of the message (in bytes) |
| Expose data | Flag indicating if endpoints GET /data and DELETE /data should be exposed |
Custom
Custom endpoint type allows the users to provide own endpoint type implementation.
Message Content Types
The receiver can accept messages in various formats. Currently, there are four different options available:
- JSON
- XML
- CSV
- Binary Q15 (Little-Endian)
- Vibration sensor
CSV
For CSV, it is possible to specify Values separator, Device ID column index (default 0) and Encoding (default UTF-8).
For Bulk mode, two additional parameters are available: Row length and Row separator.
- Row separator - defines the end of a row, EOL (\n) by default.
- Row length - if defined, row separator is ignored and row array is splitted into subarrays with length defined by this parameter.
When the CSV is message is accepted by the receiver, it is converted to a JSON with following structure:
Source CSV message
Error rendering macro 'code': Invalid value specified for parameter 'com.atlassian.confluence.ext.code.render.InvalidValueException'F4-B8-5E-3D-92-TEST97,1551884028,54546561,153
Result in JSON
Error rendering macro 'code': Invalid value specified for parameter 'com.atlassian.confluence.ext.code.render.InvalidValueException'{"sensorId":"F4-B8-5E-3D-92-TEST97","value1":"F4-B8-5E-3D-92-TEST97","value2":"1551884028","value3":"54546561","value4":"153"}This allows the user to work with the values on both receiver and sender (by using e.g. the value2 for message rules, action rules etc.).
Binary Q15 (Little-Endian)
Receivers using this content type accept data in binary form.
Sample message
Error rendering macro 'code': Invalid value specified for parameter 'com.atlassian.confluence.ext.code.render.InvalidValueException'01001101,01010001,01010100,1010100,01000010,01101111,01111000,01001101,01010001,01010100,1010100,01000010,01101111,01111000,01101111,01111000
Result in JSON
Error rendering macro 'code': Invalid value specified for parameter 'com.atlassian.confluence.ext.code.render.InvalidValueException'{ch.A.raw: 20813,
ch.A.hex: "514d",
ch.A.dec: 0.635162353515625,
ch.B.raw: 21588,
ch.B.hex: "5454",
ch.B.dec: 0.6588134765625,
ch.C.raw: 28482,
ch.C.hex: "6f42",
ch.C.dec: 0.86920166015625,
ch.D.raw: 19832,
ch.D.hex: "4d78",
ch.D.dec: 0.605224609375,
ch.E.raw: 21585,
ch.E.hex: "5451",
ch.E.dec: 0.658721923828125,
ch.F.raw: 16980,
ch.F.hex: "4254",
ch.F.dec: 0.5181884765625,
ch.G.raw: 30831,
ch.G.hex: "786f",
ch.G.dec: 0.940887451171875,
ch.H.raw: 30831,
ch.H.hex: "786f",
ch.H.dec: 0.940887451171875,
}Number of records to auto-pause receiver
When this number of messages is reached in the local receiver database file, the receiver will automatically pause itself. When this number drop to quarter, the receiver will auto-resume.